A Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) sensor, also known as a tire pressure monitor sensor, is a critical component of a vehicle’s safety system. It is designed to monitor the air pressure in each tire and alert the driver if any tire is underinflated, which can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, uneven tire wear, and increased risk of tire failure.
How Does a Tire Pressure Monitor Sensor Work?
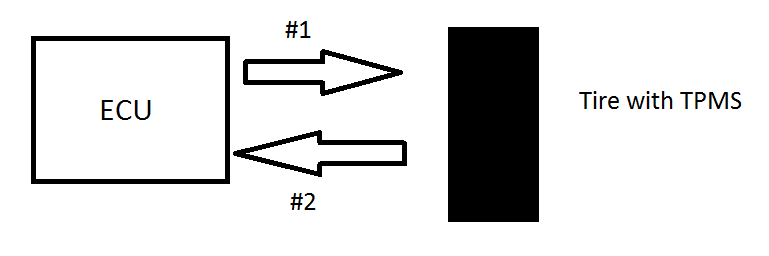
A TPMS sensor typically consists of a pressure sensor, a microcontroller, and a transmitter. The pressure sensor measures the air pressure inside the tire, and the microcontroller processes this data. If the pressure falls below a predetermined threshold, the microcontroller sends a signal to the transmitter, which then sends a wireless signal to the vehicle’s onboard computer. The onboard computer then illuminates a warning light on the dashboard to alert the driver of low tire pressure.
The pressure sensor in a TPMS sensor is typically a piezoelectric or piezoresistive device that converts the mechanical force of the tire pressure into an electrical signal. The microcontroller then processes this signal and compares it to the predetermined pressure threshold. If the pressure is too low, the microcontroller triggers the transmitter to send a wireless signal to the vehicle’s onboard computer.
The wireless signal transmitted by the TPMS sensor is typically in the 315 MHz or 433 MHz frequency range, which is a common frequency used for short-range wireless communication in automotive applications. The onboard computer in the vehicle receives this signal and processes it to determine which tire is underinflated and displays the appropriate warning light on the dashboard.
Types of TPMS Sensors

There are two main types of TPMS sensors: direct and indirect.
Direct TPMS Sensors
Direct TPMS sensors are installed directly inside the tire and measure the air pressure directly. They provide accurate, real-time pressure readings and can also monitor tire temperature. Each sensor has a unique serial number, allowing the system to distinguish between different tires and vehicles.
Direct TPMS sensors are typically powered by a small battery that can last for up to 10 years, depending on the usage and manufacturer. They are designed to withstand the harsh environment inside the tire, including high temperatures, vibrations, and exposure to various chemicals and materials.
One of the key advantages of direct TPMS sensors is that they are not affected by tire rotations or replacements. This means that the system can accurately track the pressure in each individual tire, even if the tires are rotated or replaced. This makes it easier to maintain the TPMS system and ensures that the driver is always alerted to any underinflated tires.
Indirect TPMS Sensors
Indirect TPMS sensors use the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) to measure wheel speed and estimate tire pressure. They are less accurate than direct sensors and can be affected by tire rotations or replacements.
Indirect TPMS sensors work by monitoring the rotational speed of each wheel. If one tire is underinflated, it will have a slightly different rolling radius than the other tires, which will cause it to rotate at a different speed. The indirect TPMS system can detect these differences in wheel speed and use them to estimate the tire pressure.
While indirect TPMS sensors are generally less accurate than direct sensors, they can be a more cost-effective solution for some vehicle manufacturers. They also do not require the installation of individual sensors in each tire, which can simplify the installation process.
Advantages of Direct TPMS Sensors
- Accurate Pressure Readings: Direct TPMS sensors provide actual tire pressure readings from inside the tire, which are more accurate than the estimates provided by indirect TPMS sensors.
- Not Prone to Inaccuracies: Direct TPMS sensors are not affected by tire rotations or replacements, ensuring that the system can accurately track the pressure in each individual tire.
- Simple Resynchronization: Resynchronizing the TPMS system after a tire rotation or replacement is a simple process with direct TPMS sensors, as the system can easily identify the new location of each sensor.
- Long Battery Life: The batteries inside direct TPMS sensors can last for up to 10 years, depending on the manufacturer and usage, reducing the need for frequent sensor replacements.
- Spare Tire Inclusion: Many vehicles equipped with direct TPMS sensors also include a sensor in the spare tire, allowing the system to monitor the pressure in the spare as well.
Technical Specifications of TPMS Sensors
- Operating Frequency: TPMS sensors typically operate at a frequency of 315 MHz or 433 MHz, which is a common frequency used for short-range wireless communication in automotive applications.
- Sensor Battery Life: The battery life of TPMS sensors can range from 5 to 10 years, depending on the manufacturer and usage. Some sensors may have replaceable batteries, while others may be designed to be replaced entirely when the battery runs out.
- Pressure Measurement Range: TPMS sensors can measure tire pressure from 0 to 120 psi (0 to 827 kPa), which covers the typical range of tire pressures used in passenger vehicles.
- Temperature Measurement Range: Some TPMS sensors can measure tire temperature from -40°C to 125°C (-40°F to 257°F), which allows the system to monitor the tire’s operating conditions and provide additional data to the vehicle’s onboard computer.
- Sensor Dimensions: TPMS sensors are typically small, compact devices that are designed to fit inside the tire’s valve stem or on the wheel rim. The dimensions can vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific vehicle application, but they are generally less than 2 inches (50 mm) in diameter and less than 1 inch (25 mm) in height.
- Sensor Weight: The weight of a TPMS sensor can range from 10 to 30 grams, depending on the design and materials used. This lightweight design helps to minimize the impact on the vehicle’s handling and fuel efficiency.
- Sensor Durability: TPMS sensors are designed to withstand the harsh environment inside the tire, including high temperatures, vibrations, and exposure to various chemicals and materials. They are typically made of durable materials such as aluminum or stainless steel to ensure long-term reliability.
Reference:
- https://www.bridgestonetire.com/learn/maintenance/tire-pressure-monitoring-system-how-tpms-works/
- https://www.autozone.com/engine-management/tire-pressure-monitoring-sensor
- https://www.americastire.com/accessories/tpms/tpms-sensors-catalog
