Height sensor diagrams represent sophisticated electronic mapping systems that translate physical displacement into precise electrical signals. These intricate devices capture spatial measurements across multiple industries, utilizing advanced sensing technologies like ultrasonic, capacitive, and laser mechanisms to determine accurate distance and positioning information with remarkable precision and reliability.
What Are Height Sensor Diagrams?
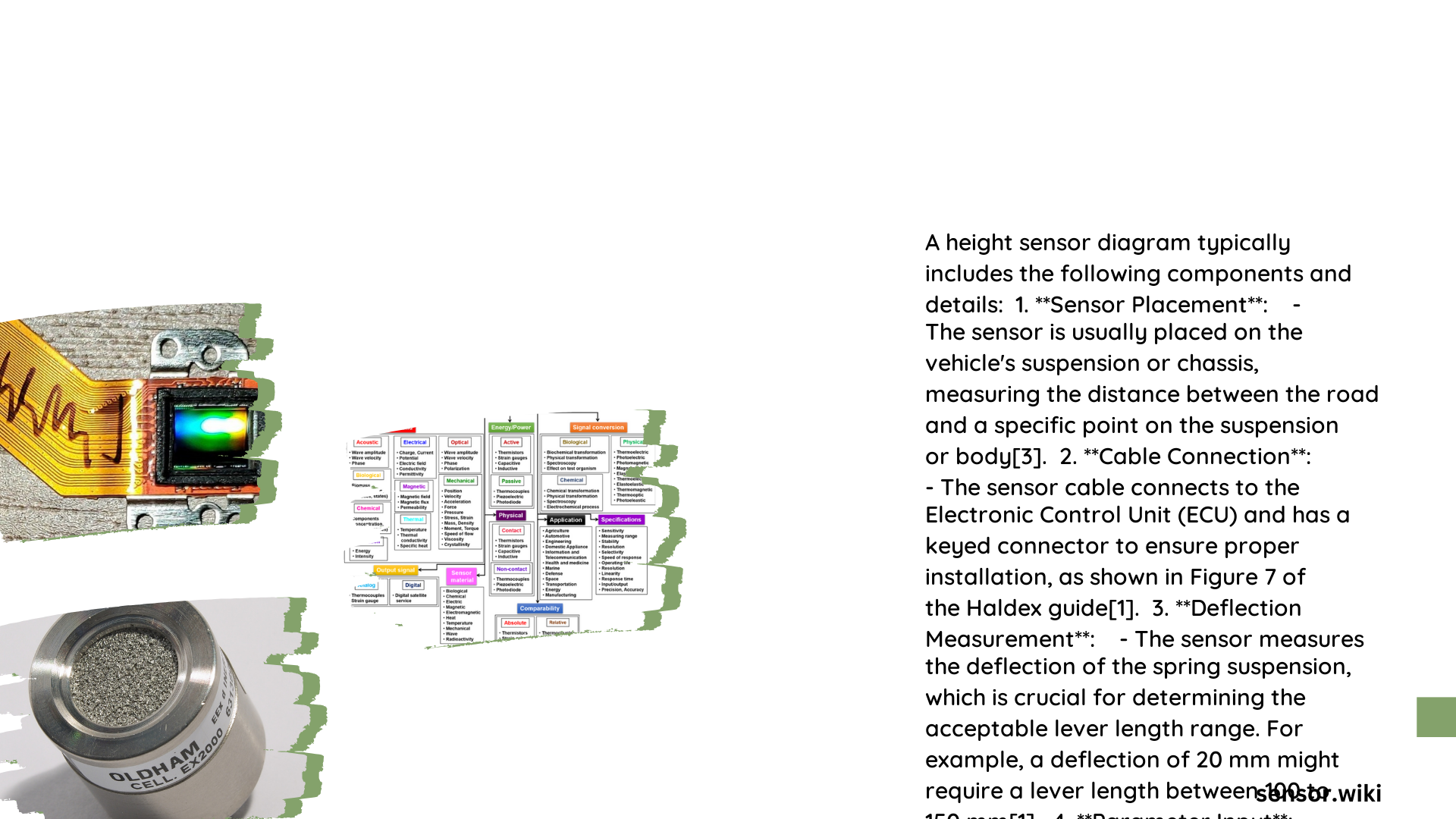
Height sensor diagrams provide comprehensive visual representations of sensor components, electrical connections, and operational mechanisms. These technical illustrations help engineers, technicians, and researchers understand complex sensor architectures and implementation strategies.
How Do Height Sensors Function?
Fundamental Working Principles
Height sensors operate through multiple detection methodologies:
- Time-of-Flight Mechanism
- Measures signal return time
- Calculates distance using wave propagation principles
-
Applicable in ultrasonic and laser technologies
-
Capacitive Detection
- Tracks electrical capacitance variations
- Provides high-precision measurements
-
Minimal environmental interference
-
Infrared Reflection
- Compares reflected light intensity
- Suitable for short-range measurements
- Common in 3D printing applications
What Components Comprise Height Sensor Diagrams?
Key Structural Elements
| Component | Function | Typical Material |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Body | Housing primary electronics | Aluminum/Plastic |
| Linkage | Mechanical movement translator | Stainless Steel |
| Electrical Connectors | Signal and power transmission | Copper Alloy |
| Mounting Bracket | Structural attachment | Reinforced Polymer |
Where Are Height Sensors Implemented?
Diverse Application Domains
Height sensors find critical applications across multiple sectors:
- Automotive Industry
- Suspension height monitoring
- Vehicle leveling systems
-
Active ride control
-
Robotics
- Precision positioning
- Object detection
-
Navigation assistance
-
Manufacturing
- Quality control measurements
- Automated assembly processes
- Material thickness verification
What Are Sensor Measurement Characteristics?
Performance Specifications
Height sensors demonstrate remarkable technical capabilities:
- Accuracy Range: ±0.01mm to ±5mm
- Operational Frequency: 10-1000 Hz
- Power Consumption: 10-50mA
- Temperature Tolerance: -40°C to +125°C
How Are Height Sensors Wired?
Electrical Configuration
Typical height sensor wiring involves:
- Power Input (+12V)
- Ground Connection
- Signal Output Channel
- Optional Auxiliary Interfaces
What Challenges Exist in Height Sensor Design?
Technical Considerations
Engineers must address:
– Environmental durability
– Signal interference mitigation
– Calibration complexity
– Cost-effective manufacturing
Emerging Technological Trends
Height sensor technologies continue evolving with:
– Miniaturization
– Enhanced computational algorithms
– Improved material sciences
– Integration with artificial intelligence
Conclusion
Height sensor diagrams represent sophisticated engineering solutions bridging physical measurements with electronic interpretations, enabling unprecedented precision across diverse technological domains.
References:
- [CTS Corporation Sensor Documentation]
- [Automotive Height Sensing Technical Journals]
- [Industrial Sensor Application Reports]
